ML Introduction
Preprocessing
Regression
Classification
Encoding Categorical Variables in Machine Learning

Encoding Categorical Variables

Encoding Categorical Variables
Encoding Categorical Variables means Converting categorical variables into numerical values.
Encoding categorical variables is a crucial step in data preprocessing.
Machine learning algorithms require numerical input, so categorical data must be transformed into a numerical format.
Encoding Common techniques include Label Encoding and One-Hot Encoding.
There are also different encoding techniques, but in this video, we cover only Label encoding and One-Hot encoding.
- Label Encoding: Assigning a unique integer to each category.
- One-Hot Encoding: Creating binary columns for each category.
Label Encoding
Label encoding assigns a unique integer to each category.
While it's simple, it can create an ordinal relationship between categories that doesn't exist.
Using the fit_transform() function from the LabelEcncoder class, convert Python array categorical values into numeric values.
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
data = ["cat", "dog", "mouse"]
# Label encoding
label_encoder = LabelEncoder()
encoded_data = label_encoder.fit_transform(data)
print(encoded_data)
[0 1 2]
After running, the Python array categorical variables are converted into unique integer values.
Apply label encoding to categorical columns in the data frame
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
df = pd.read_csv("home_price_prediction.csv")
encoder = LabelEncoder()
encode_data = encoder.fit_transform(df["location"])
df["new_location"] = encode_data
df

The new encoded values are displayed in the data frame.
One-Hot Encoding
One-hot encoding creates a new binary feature for each category.
This method avoids ordinal relationships and is widely used.
Using the get_dummies() function from the panda's library we apply one hot encoding on the animal column.
import pandas as pd
data = pd.DataFrame({"animal": ["cat", "dog", "mouse"]})
# One-hot encoding
one_hot_encoded_data = pd.get_dummies(data)
print(one_hot_encoded_data)
animal_cat animal_dog animal_mouse
0 1 0 0
1 0 1 0
2 0 0 1
After running, the three columns are created corresponding to the values of an animal column.
If the value is present, set the numeric value to 1, and the rest is 0 in every column.
Apply one-hot encoding to categorical columns in the data frame
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv("home_price_prediction.csv")
one_hot_encoded_data = pd.get_dummies(df["location"])
new_df = df.join(one_hot_encoded_data)
new_df
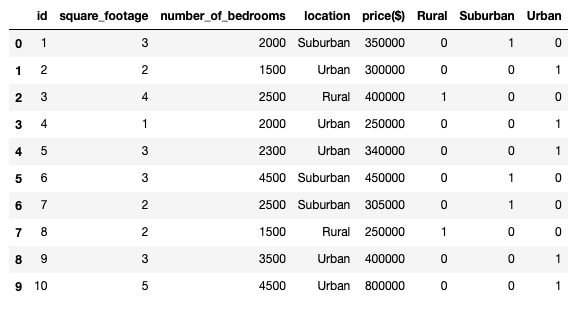
The new encoded values are displayed in the data frame.
The result is similar if the corresponding value is present then it takes the numeric value 1, otherwise it takes 0.